Avoid NYCRR Infractions

In 2017, the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) launched GDPR-like cybersecurity regulations for its massive financial industry. This new regulation lays-out reporting requirements in the event of a data-breach and limitations regarding retaining data.
23 NYCRR 500 issues uniformed guidelines on a number of measures to undertake for enhanced data protection. Some of the requirements include regular risk assessment, documenting and enforcing cybersecurity policies, designate a full-time or part-time Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), conduct periodic tests, and more.
The NYCRR primarily contains state agency rules and regulations adopted under the State Administrative Procedure Act (SAPA). The 23 Titles include one for each state department, one for miscellaneous agencies and one for the Judiciary. The Office of Court Administration and the Judiciary are exempt from SAPA requirements.
The NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation (23 NYCRR 500) is “designed to promote the protection of customer information as well as the information technology systems of regulated entities”.
Cyber criminals have been hyper-active over the last few years in targeting multiple different industries with malware, ransomware, phishing, and other cyberattacks. The financial institutions across the globe have been badly affected by the surge in such attacks. New York has been at the epicenter of many such cyberattacks which has results in huge financial losses, severe damage in reputation, and in some cases even bankruptcy. In response to this ever-growing cybersecurity threat environment, the NYDFS issued the final Cybersecurity Regulation (23 NYCRR Part 500) to standardize security measures across covered entities. The objective is to have proper security policies and procedures in place to better protect client data against breach and to encourage higher standards security across the board.
23 NYCRR 500 Timeline: The regulation went into effect on March 1, 2017, with implementation to occur within 180 days (August 28, 2017); it affects entities regulated by the New York Department of Financial Services (DFS).
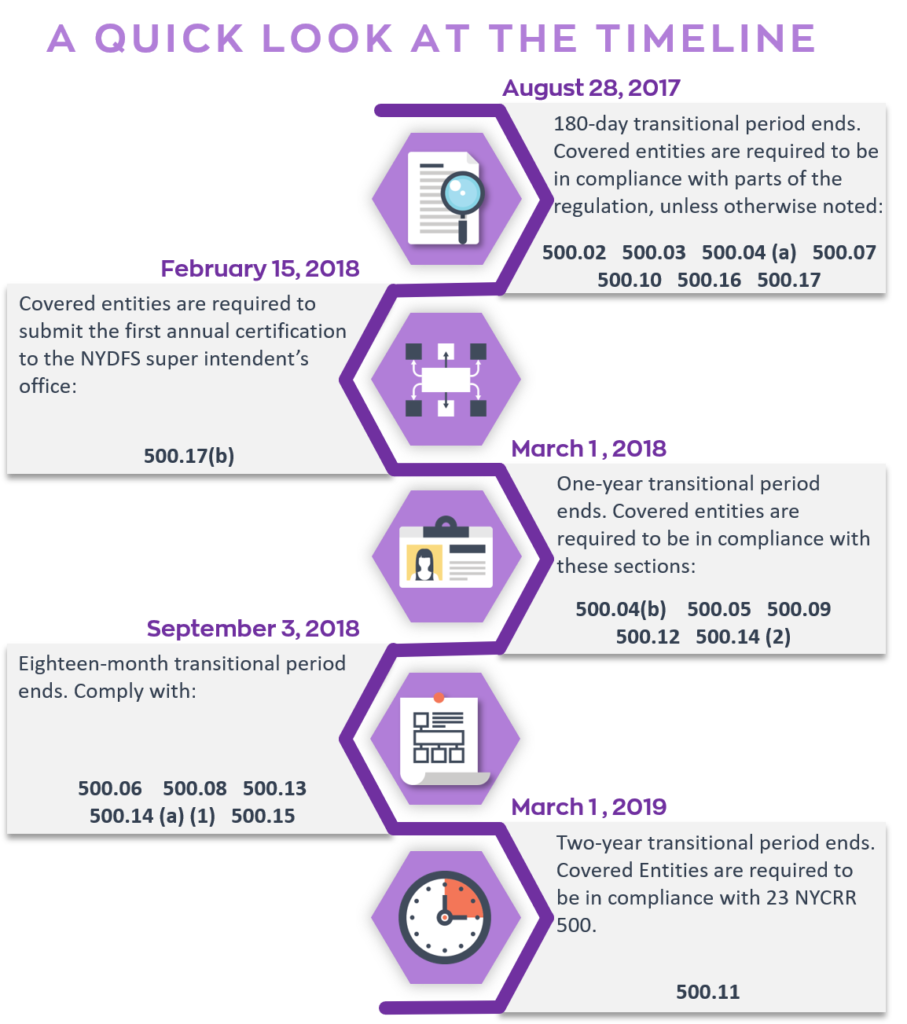
The requirements outlined by this new regulation include:
The NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation covers any organization operating in the state of New York under authorization of the Banking Law, the Insurance Law, or the Financial Services law.
This includes:

Certain entities that do not handle classes of nonpublic information are also exempt from certain provisions. 23 NYCRR 500.19(c) and (d).
If an entity qualifies for one of the exemptions, it must file a Notice of Exemption within 30 days of the determination of the exemptions 23 NYCRR 500.19(e).
The NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation (23 NYCRR 500) contains a new set of rules that emphasizes all cybersecurity requirements for all financial organizations.
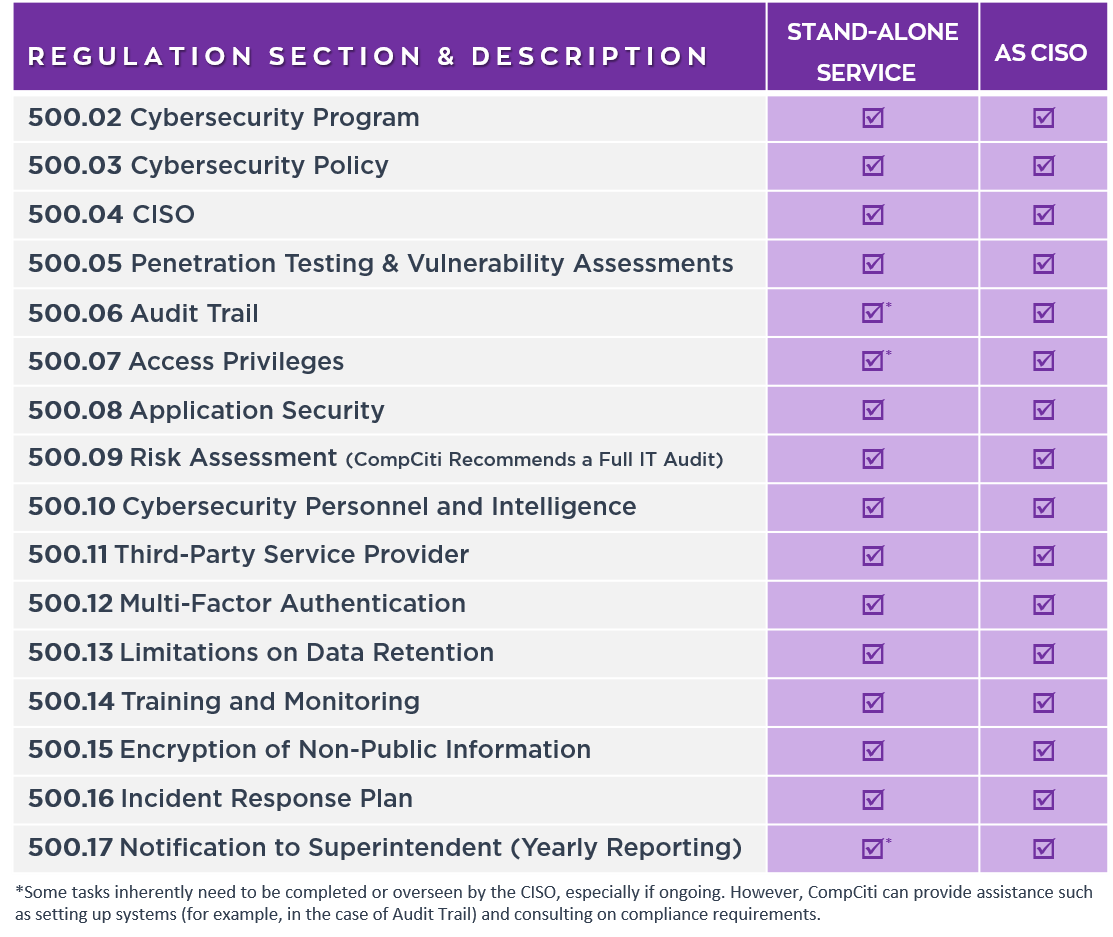
The regulation is outlined to market the protection of client information in addition to information technology systems of regulated entities”. A checklist of all NYDFS Cyber Security requirements is described as follows:
Section 500.02 – Cybersecurity Program
Section 500.03 – Cybersecurity Policies
Section 500.04 – Chief Information Security Officer
Section 500.05 – Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Management
Section 500.06 – Audit Trail
Section 500.07 – Access Privileges
Section 500.08 – Application Security
Section 500.09 – Risk Assessments
Section 500.10 – Cybersecurity Personnel and Intelligence
Section 500.12 – Multi-Factor Authentication
Section 500.13 – Data Retention Limitations
Section 500.14 – Training and Observation
Section 500.15 – Encryption of Confidential Information
Section 500.16 – Incident Response Plan
Section 500.17 – Superintendent Notification

According to the new cyber security NYDFS regulations, it is mandatory for all covered entities to implement and file the regulations by August 28th, 2017. Those who are not compliant by this deadline will be penalized. The Compliance Experts at CompCiti will not only ensure that you are compliant, but will help you to implement a more effective, long-term cyber security protocol in the process.
CompCiti provides its clients with CISA-certified IT auditing services. We offer a range of services from IT auditing to helping you address any cybersecurity issues identified during the audit. CompCiti can also act as your Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), taking care of all the details to ensure compliance.
An IT audit is similar to a financial audit in that it helps ensure your company is following best cybersecurity practices. An IT audit includes a Risk Assessment for cyber threats (as required by 23 NYCRR Part 500), but it also is designed to find holes in your cybersecurity, review software update policies, and more to ensure your client data is secure. Most importantly, a comprehensive IT audit gives you the full picture of your current cybersecurity preparedness, allowing you to develop a more effective Cybersecurity Program and Cybersecurity Policy than you could with a Risk Assessment alone.
Contact CompCiti today for a free needs assessment. We’ll explain to you what you need to meet full DFS compliance and how we can help you every step of the way.

You must report events that have a “reasonable likelihood of materially harming any material part” of the company’s IT infrastructure.
Covered entities are required to conduct assessment at least once a year. However, it is recommended to conduct “periodic” assessments to ensure safeguard.
The purpose of this entire exercise is to bring uniformity to measures taken by financial institutions to better protect themselves against imminent cybersecurity threats. There are significant documentation required to achieve this standard. Right from preparing for incident reporting to presenting company’s risk assessment report, the CISO is required to handle a lengthy root of documentation. Upon identifying a potential threat, the CIO is also responsible to document remediation efforts undertaken to ensure the threat is neutralized.
